Dissertations / Theses on the topic 'Ising'
Create a spot-on reference in APA, MLA, Chicago, Harvard, and other styles
Consult the top 50 dissertations / theses for your research on the topic 'Ising.'
Next to every source in the list of references, there is an 'Add to bibliography' button. Press on it, and we will generate automatically the bibliographic reference to the chosen work in the citation style you need: APA, MLA, Harvard, Chicago, Vancouver, etc.
You can also download the full text of the academic publication as pdf and read online its abstract whenever available in the metadata.
Browse dissertations / theses on a wide variety of disciplines and organise your bibliography correctly.
Giokas, Philip. "Aspects of the Ising and tricritical Ising models." Thesis, King's College London (University of London), 2013. https://kclpure.kcl.ac.uk/portal/en/theses/aspects-of-the-ising-and-tricritical-ising-models(8bb2e06f-aef7-45ca-8058-3a3eea92b9e6).html.
Full textLi, Chengshu. "Tricritical Ising edge modes in a Majorana-Ising ladder." Thesis, University of British Columbia, 2017. http://hdl.handle.net/2429/62467.
Full textScience, Faculty of
Physics and Astronomy, Department of
Graduate
Karevski, Dragi. "Ising Quantum Chains." Habilitation à diriger des recherches, Université Henri Poincaré - Nancy I, 2005. http://tel.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-00113500.
Full textKamenetsky, Dmitry, and dkamen@rsise anu edu au. "Ising Graphical Model." The Australian National University. ANU College of Engineering and Computer Science, 2010. http://thesis.anu.edu.au./public/adt-ANU20100727.221031.
Full textHystad, Grethe. "Periodic Ising Correlations." Diss., The University of Arizona, 2009. http://hdl.handle.net/10150/196130.
Full textVarrassi, Lorenzo. "Il modello di Ising." Bachelor's thesis, Alma Mater Studiorum - Università di Bologna, 2016. http://amslaurea.unibo.it/10573/.
Full textMalmini, Ranasinghe P. K. C. "Gonihedric 3D Ising models." Thesis, Heriot-Watt University, 1997. http://hdl.handle.net/10399/675.
Full textPugh, Mathew. "Ising model and beyond." Thesis, Cardiff University, 2008. http://orca.cf.ac.uk/54791/.
Full textPaula, Gilberto Luiz de Souza. "Modelos de Ising dinamico." reponame:Repositório Institucional da UFSC, 1994. http://repositorio.ufsc.br/xmlui/handle/123456789/76170.
Full textMade available in DSpace on 2012-10-16T07:56:41Z (GMT). No. of bitstreams: 0Bitstream added on 2016-01-08T18:59:08Z : No. of bitstreams: 1 96497.pdf: 1094541 bytes, checksum: cb7b6164b0d0951706f97e2c507d68c1 (MD5)
Nesta dissertação estudamos o comportamento dinâmico de dois modelos ferromagnéticos através da equação mestra. No primeiro deles consideramos o modelo de Ising num gradiente de temperatura e determinamos os estados estacionários através das prescrições de Metropolis e Glauber. Mostramos que na ausência de correlações os estados estacionários são diferentes, enquanto que levando-se em conta correlações entre primeiros vizinhos os estados estacionários são os mesmos. No segundo modelo, determinamos o diagrama de fases do modelo de Ising dinâmico em um campo aleatório na situação estacionária. Mostramos que os estados estacionários coincidem com os de equilíbrio para todo o espaço de parâmetros com exceção das vizinhanças das transições de primeira ordem.
Iberti, Massimo. "Ising-Kac models near criticality." Thesis, University of Warwick, 2018. http://wrap.warwick.ac.uk/109480/.
Full textDikkala, Sai Nishanth. "Testing properties of Ising models." Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 2017. http://hdl.handle.net/1721.1/108844.
Full textThis electronic version was submitted by the student author. The certified thesis is available in the Institute Archives and Special Collections.
Cataloged from student-submitted PDF version of thesis.
Includes bibliographical references (pages 99-102).
Given samples from an unknown multivariate distribution p, is it possible to distinguish whether p is the product of its marginals versus p being [epsilon]-far from every product distribution? Similarly, is it possible to distinguish whether p equals a given distribution q versus p and q being [epsilon]-far from each other? These problems of testing independence and goodness-of- fit have received enormous attention in statistics, information theory, and theoretical computer science, with sample-optimal algorithms known in several interesting regimes of parameters [14, 15, 17, 18, 20]. Unfortunately, it has also been understood that these problems become intractable in large dimensions, necessitating exponential sample complexity. Motivated by the exponential lower bounds for general distributions as well as the ubiquity of Markov Random Fields (MRFs) in the modeling of high-dimensional distributions, we study distribution testing on structured multivariate distributions, and in particular the prototypical example of MRFs: the Ising Model. We demonstrate that, in this structured setting, we can avoid the curse of dimensionality, obtaining sample and time efficient testers for independence and goodness-of-fit which yield a sample complexity of poly(n)=[epsilon]2 on n-node Ising models. Along the way, we develop new tools for establishing concentration of functions of the Ising model, using the exchangeable pairs framework developed by Chatterjee [27], and improving upon this framework. In particular, we prove tighter concentration results for multi-linear functions of the Ising model in the high-temperature regime. We also prove a lower bound of n=[epsilon] on the sample complexity required for testing uniformity and independence of n-node Ising models.
by Sai Nishanth Dikkala.
S.M.
Silva, Romero Tavares da. "ALEATORIEDADE EM MODELOS DE ISING." Universidade de São Paulo, 1993. http://www.teses.usp.br/teses/disponiveis/43/43133/tde-22052012-133450/.
Full textIn the first part of this work we propose a dynamical mean field approximation to analyse Ising models with elements of randomnss, defined by discret probability functions. We have analysed the random field model (S = 1/2); the random bond model (S = 1/2); the site diluted model (S = 3/2) and the random crystal field model (S = 1), obtaining the respective phase diagrams. In the second part we have analysed spinglass models (S = 3/2) in the presence of a crystal field. We have studied the van Hemmen and the classic spin glass model à la Sherrington and Kirkpatrick, using replica symmetric scheme, to obtain the corresponding phase diagrams.
Tamashiro, Mário Noboru. "Modelos de Ising com Competição." Universidade de São Paulo, 1996. http://www.teses.usp.br/teses/disponiveis/43/43133/tde-28022014-163442/.
Full textIn this work we consider three Ising models with competition: which is generated by dynamical couplings of antagonistic character, by the geometry of the underlying lattice, or by interactions of competitive uniaxial periodicities and disorder elements. The first model, for which equilibrium statistical mechanics techniques do not apply, consists in a fully connected attractor neural network storing p = 2 patterns, whose temporal evolution can be described (in the case of synchronous updating) by a two-dimensional dissipative mapping. The second model refers to the classic problem of the Ising antiferromagnet on the triangular lattice in the presence of a uniform magnetic field, which is investigated by various approximations - in particular, by a Bethe-Peierls approximation considering three interpenetrating equivalent sublattices. The third model, introduced to investigate the effects of quenched disorder in a modulated magnetic system, is defined by the ANNNI model in a random field. Initially we consider an analogous of this model on a Cayley tree, in the infinite-coordination limit, which can be formulated in terms of a two-dimensional dissipative mapping. Next, we consider a mean-field version on a simple cubic lattice, which allows for an analysis of the first-order transition surfaces and tricritical lines.
Marsolais, Annette M. "The Equivalence Between the Kitaev, the Transverse Quantum Ising Model and the Classical Ising Model." University of Akron / OhioLINK, 2021. http://rave.ohiolink.edu/etdc/view?acc_num=akron1619792923386843.
Full textRidderstolpe, Ludwig. "Exact Solutions of the Ising Model." Thesis, Uppsala universitet, Teoretisk astrofysik, 2017. http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:uu:diva-329081.
Full textLacasse, Martin Daniel. "Exact dynamics of small Ising systems." Thesis, McGill University, 1994. http://digitool.Library.McGill.CA:80/R/?func=dbin-jump-full&object_id=28814.
Full textWe at first examine one- and two-dimensional systems using periodic boundary conditions. Systems with free boundary conditions were also studied, and their results were equivalent with respect to the dynamical critical properties of the system. The effects of conservation laws were also investigated and both conserved and non-conserved systems were studied. Both local and non-local spin-exchange dynamics were investigated for conserved systems. Finally, our approach was used to simulate quenches on small systems.
This method is them used to analyze phenomenological transformations done by dynamical renormalization-group (RG) methods. It is found that, when the RG transformation is linear in probability space, there exists a corresponding Markov chain generating the time sequence of the renormalized systems. An example is given for the one-dimensional Ising model.
Smith, Thomas H. R. "Driven interfaces in the Ising model." Thesis, University of Bristol, 2010. http://ethos.bl.uk/OrderDetails.do?uin=uk.bl.ethos.535182.
Full textGray, Sean. "Bootstrapping the Three-dimensional Ising Model." Thesis, Uppsala universitet, Teoretisk fysik, 2017. http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:uu:diva-322146.
Full textMilanesi, Paolo. "Sur la métastabilité de la dynamique de Glauber." Thesis, Aix-Marseille, 2018. http://www.theses.fr/2018AIXM0663.
Full textIn this thesis we study the metastable behavior of the Glauber dynamics for the two-dimensional Ising model in the regime where the temperature is kept fixed at some subcritical value and the external magnetic field is vanishing.In the infinite volume regime, this model has been studied by Schonmann and Shlosman who show the connection between the mean transition time and the integrated surface tension of the Wulff shape. However, the exponentiality of the transition time, already in the finite volume case, is still an open problem. In this thesis we address this question.First, we give a theoretical framework to deal with metastable markovian dynamics such that the support of the metastable measure is not reducible to a single configuration. Our techniques allow to get the exponential law of the transition time as well as to estimate its mean and the relaxation time of the dynamics. In the second part of the thesis we address the metastable Glauber dynamics; we give suitable definitions of the metastable and the stable sets and we estimate the relaxation time of the dynamics restricted to these two sets. In doing so, we are in good shape to exploit the techniques studied in the first part of our work. Our results hold true for any subcritical temperature and a wide class of starting measures
Pomponio, Octavio. "Transizioni di fase nel modello di Ising." Bachelor's thesis, Alma Mater Studiorum - Università di Bologna, 2015. http://amslaurea.unibo.it/9562/.
Full textHausmann, Johannes. "Statistical mechanics of strongly driven Ising systems." [S.l.] : [s.n.], 2001. http://deposit.ddb.de/cgi-bin/dokserv?idn=963559311.
Full textZhang, Xingjun. "Critical Properties of Small World Ising Models." MSSTATE, 2005. http://sun.library.msstate.edu/ETD-db/theses/available/etd-11102005-220554/.
Full textSakellariou, Jason. "Inverse inference in the asymmetric Ising model." Phd thesis, Université Paris Sud - Paris XI, 2013. http://tel.archives-ouvertes.fr/tel-00869738.
Full textCornell, Stephen John. "Studies of freezing in kinetic Ising models." Thesis, University of Oxford, 1990. http://ethos.bl.uk/OrderDetails.do?uin=uk.bl.ethos.257825.
Full textBrown, A. S. "Critical phenomena in the Random Ising Model." Thesis, University of Edinburgh, 1986. http://ethos.bl.uk/OrderDetails.do?uin=uk.bl.ethos.370906.
Full textDinóla, Isabel Cristina Souza. "Super Antiferromagneto de Ising com campo uniforme." Universidade Federal do Amazonas, 2009. http://tede.ufam.edu.br/handle/tede/4543.
Full textApproved for entry into archive by Divisão de Documentação/BC Biblioteca Central (ddbc@ufam.edu.br) on 2015-08-07T13:20:19Z (GMT) No. of bitstreams: 1 Dissertação - Isabel Cristina Souza Dinóla.pdf: 562066 bytes, checksum: fb6aeda0c4854690f169abad1c217b8d (MD5)
Approved for entry into archive by Divisão de Documentação/BC Biblioteca Central (ddbc@ufam.edu.br) on 2015-08-07T13:24:35Z (GMT) No. of bitstreams: 1 Dissertação - Isabel Cristina Souza Dinóla.pdf: 562066 bytes, checksum: fb6aeda0c4854690f169abad1c217b8d (MD5)
Made available in DSpace on 2015-08-07T13:24:35Z (GMT). No. of bitstreams: 1 Dissertação - Isabel Cristina Souza Dinóla.pdf: 562066 bytes, checksum: fb6aeda0c4854690f169abad1c217b8d (MD5) Previous issue date: 2009-05-22
CAPES - Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior
The phase diagram of the two-dimensional super-antiferromagnetic (SAF) Ising model in the presence of a magnetic field is investigated within the framework of a real-space renormalization-group approximation. We consider nearest neighbor ferromagnetic interactions along the x(y) direction and antiferromagnetic interactions in the y(x) direction. The system presents a ordered phase at low temperatures and zero fields. The presence of a magnetic field induces a competition between the energy interactions of the SAF Hamiltonian. The resulting behavior has been a matter of controversy in the last years. We depicted the main results in the magnetic field versus temperature phase diagram. A second-order transition line separates a super-antiferromagnetic phase from a field induced ferromagnetic phase. Our study reveals that the magnetic field induces a phase transition at a single temperature value, thus, we did not find any evidence of reentrant behavior as claimed by some authors.
Utilizamos uma técnica de grupo de renormalização no espaço real para estudar o sistema super antiferromagneto (SAF) de Ising bidimensional sob a influência de um campo magnético externo. Neste modelo as interações de primeiros vizinhos na direção x são ferromagnéticas e na direção y são antiferromagnéticas. Este sistema apresenta uma fase ordenada, para baixas temperaturas e campos nulos, com uma estrutura de linhas ferromagnéticas e colunas antiferromagnéticas. A aplicação do campo magnético induz uma competição entre as energias de interação do modelo e o comportamento resultante desta competição tem sido objeto de estudo e gerado algumas controvérsias nos últimos anos. Na presença do campo magnético observa-se, além da fase SAF, a fase ferromagnética induzida pelo campo (FIC). Apresentamos neste trabalho o diagrama de fases completo do sistema SAF no plano temperatura versus campo magnético. O diagrama de fases obtido mostra uma linha de transição de segunda ordem separando a fase SAF da fase FIC. Nossos resultados contrariam resultados anteriores que preveêm um comportamento reentrante no diagrama de fases do sistema SAF.
Feng, Shuangtong. "Efficient Parallelization of 2D Ising Spin Systems." Thesis, Virginia Tech, 2001. http://hdl.handle.net/10919/36263.
Full textIn this thesis,we designed and implemented a variety of parallel algorithms for both sweep spin selection and random spin selection. We analyzed our parallel algorithms on a portable and general parallel machine model, namely the LogP model. We were able to obtain rigorous theoretical run-times on LogP for all the parallel algorithms. Moreover, a guiding equation was derived for choosing data layouts (blocked vs. stripped) for sweep spin selection. In regards to random spin selection, we were able to develop parallel algorithms with efficient communication schemes. We analyzed randomness of our schemes using statistical methods and provided comparisons between the different schemes. Furthermore, algorithms were implemented and performance data gathered and analyzed in order to determine further design issues and validate theoretical analysis.
Master of Science
Björnberg, Jakob Erik. "Graphical representations of Ising and Potts models stochastic geometry of the quantum Ising model and the space-time Potts model /." Stockholm : Skolan för teknikvetenskap, Kungliga Tekniska högskolan, 2009. http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:kth:diva-11267.
Full textBjörnberg, Jakob Erik. "Graphical representations of Ising and Potts models : Stochastic geometry of the quantum Ising model and the space-time Potts model." Doctoral thesis, KTH, Matematik (Inst.), 2009. http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:kth:diva-11267.
Full text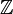 . In Chapter 3 we develop an alternative graphical representation of the quantum Ising model, called the random-parity representation. This representation is based on the random-current representation of the classical Ising model, and allows us to study in much greater detail the phase transition and critical behaviour. A major aim of this chapter is to prove sharpness of the phase transition in the quantum Ising model—a central issue in the theory— and to establish bounds on some critical exponents. We address these issues by using the random-parity representation to establish certain differential inequalities, integration of which gives the results. In Chapter 4 we explore some consequences and possible extensions of the results established in Chapters 2 and 3. For example, we determine the critical point for the quantum Ising model in
. In Chapter 3 we develop an alternative graphical representation of the quantum Ising model, called the random-parity representation. This representation is based on the random-current representation of the classical Ising model, and allows us to study in much greater detail the phase transition and critical behaviour. A major aim of this chapter is to prove sharpness of the phase transition in the quantum Ising model—a central issue in the theory— and to establish bounds on some critical exponents. We address these issues by using the random-parity representation to establish certain differential inequalities, integration of which gives the results. In Chapter 4 we explore some consequences and possible extensions of the results established in Chapters 2 and 3. For example, we determine the critical point for the quantum Ising model in 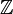 and in ‘star-like’ geometries.
and in ‘star-like’ geometries.HTML clipboard Statistisk fysik syftar till att förklara ett materials makroskopiska egenskaper i termer av dess mikroskopiska struktur. En särskilt intressant egenskap är är fenomenet fasövergång, det vill säga en plötslig förändring i de makroskopiska egenskaperna när externa förutsättningar varieras. Två modeller är särskilt intressanta för en matematiker, nämligen Ising-modellen av en magnet och perkolationsmodellen av ett poröst material. Dessa två modeller sammanförs av den så-kallade fk-modellen, en slumpgrafsmodell som först studerades av Fortuin och Kasteleyn på 1970-talet. fk-modellen har sedermera visat sig vara extremt användbar för att bevisa viktiga resultat om Ising-modellen och liknande modeller. I den här avhandlingen studeras den motsvarande grafiska strukturen hos två näraliggande modeller. Den första av dessa är den kvantteoretiska Isingmodellen med transverst fält, vilken är en utveckling av den klassiska Isingmodellen och först studerades av Lieb, Schultz och Mattis på 1960-talet. Den andra modellen är rumtid-perkolation, som är nära besläktad med kontaktmodellen av infektionsspridning. I Kapitel 2 definieras rumtid-fk-modellen, och flera probabilistiska verktyg utforskas för att studera dess grundläggande egenskaper. Vi möter rumtid-Potts-modellen, som uppenbarar sig som en naturlig generalisering av den kvantteoretiska Ising-modellen. De viktigaste egenskaperna hos fasövergången i dessa modeller behandlas i detta kapitel, exempelvis det faktum att det i fk-modellen finns högst en obegränsad komponent, samt den undre gräns för det kritiska värdet som detta innebär. I Kapitel 3 utvecklas en alternativ grafisk framställning av den kvantteoretiska Ising-modellen, den så-kallade slumpparitetsframställningen. Denna är baserad på slumpflödesframställningen av den klassiska Ising-modellen, och är ett verktyg som låter oss studera fasövergången och gränsbeteendet mycket närmare. Huvudsyftet med detta kapitel är att bevisa att fasövergången är skarp—en central egenskap—samt att fastslå olikheter för vissa kritiska exponenter. Metoden består i att använda slumpparitetsframställningen för att härleda vissa differentialolikheter, vilka sedan kan integreras för att lägga fast att gränsen är skarp. I Kapitel 4 utforskas några konsekvenser, samt möjliga vidareutvecklingar, av resultaten i de tidigare kapitlen. Exempelvis bestäms det kritiska värdet hos den kvantteoretiska Ising-modellen på
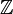 , samt i ‘stjärnliknankde’ geometrier.
, samt i ‘stjärnliknankde’ geometrier.QC 20100705
Björnberg, Jakob Erik. "Graphical representations of Ising and Potts models : stochastic geometry of the quantum Ising model and the space-time Potts model." Thesis, University of Cambridge, 2010. https://www.repository.cam.ac.uk/handle/1810/224774.
Full textAndrén, Daniel. "On the Ising problem and some matrix operations." Doctoral thesis, Umeå universitet, Institutionen för matematik och matematisk statistik, 2007. http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:umu:diva-1129.
Full textMcKenzie, Ryan. "Fluctuations and phase transitions in quantum Ising systems." Thesis, University of British Columbia, 2016. http://hdl.handle.net/2429/59105.
Full textScience, Faculty of
Physics and Astronomy, Department of
Graduate
Andrén, Daniel. "On the Ising problem and some matrix operations /." Umeå : Dept. of Mathematics and Mathematical Statistics, Umeå University, 2007. http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:umu:diva-1129.
Full textLatremoliere, Franck Thierry. "Boundaries and interfaces in the planar ising ferromagnet." Thesis, University of Oxford, 1996. http://ethos.bl.uk/OrderDetails.do?uin=uk.bl.ethos.320674.
Full textCanning, Andrew Magnus. "Ising spin models of partially connected neural networks." Thesis, University of Edinburgh, 1988. http://hdl.handle.net/1842/13304.
Full textHernandez, Hernandez Fabio 1990. "Estados de impureza no modelo de Ising quântico." [s.n.], 2016. http://repositorio.unicamp.br/jspui/handle/REPOSIP/322412.
Full textDissertação (mestrado) - Universidade Estadual de Campinas, Instituto de Física Gleb Wataghin
Made available in DSpace on 2018-08-30T18:12:28Z (GMT). No. of bitstreams: 1 Hernandez_FabioHernandez_M.pdf: 2178317 bytes, checksum: 00e18623b835112b2aa5c348e4651b65 (MD5) Previous issue date: 2016
Resumo: A descrição da dinâmica quântica de sistemas de muitos corpos é um ingrediente chave para computação e simulações quânticas. No presente projeto, estudamos a dinâmica de cadeias de spin na presença de impurezas ou defeitos. O sistema de Ising quantico (Ising com campo transverso) com uma impureza foi solucionado de forma exata. Este sistema de spins pode ser simulado de forma analítica por partículas quânticas (transformação de Jordan-Wigner). Caracterizamos o espectro, as autofunções e a evolução temporal da magnetização para estados iniciais particulares, focando no papel desempenhado pelos estados de impureza. Finalmente observamos oscilações remanescentes na magnetização, após a relaxação do sistema, para alguns valores dos parâmetros da impureza nos quais existem dois estados ligados no espectro de energias
Abstract: The description of dynamics of quantum many-body systems is a key ingredient to perform quantum computation and/or simulations of quantum behavior. In the present proposal, we study the time evolution of quantum spin chains with impurities at one of the boundaries, in order to understand the role of defects in relaxation properties. The quantum (transverse) Ising model with an impurity has been solved in exact form, using the Jordan-Wigner transformation, where spins are mapped onto spinless fermions, thus simulating analytically a spin system with particles. We completely characterize the spectrum, with the presence of bound states depending on values of the impurity parameters. We calculate the local magnetization and observe its relaxation for particular non-homogeneous initial states. Surprisingly, remanent Rabi oscillations are observed at asymptotically long times, when the spectrum displays two bound states
Mestrado
Física
Mestre em Física
1247646/2013
CAPES
Hernández, José Javier Cerda. "Ising and Potts model coupled to Lorentzian triangulations." Universidade de São Paulo, 2014. http://www.teses.usp.br/teses/disponiveis/45/45133/tde-18032015-170430/.
Full textO objetivo principal da presente tese é pesquisar : Quais são as propriedades do modelo de Ising e Potts acoplado ao emsemble de CDT? Para estudar o modelo usamos dois métodos: (1) Matriz de transferência e Teorema de Krein-Rutman. (2) Representação FK para o modelo de Potts sobre CDT e dual de CDT. Matriz de transferência permite obter propriedades espectrais da Matriz de transferência utilizando o Teorema de Krein-Rutman [KR48] sobre operadores que conservam o cone de funções positivas. Também obtemos propriedades asintóticas da função de partição e das medidas de Gibbs. Esses propriedades permitem obter uma região onde a energia livre converge. O segundo método permite obter uma região onde a curva crítica do modelo pode estar localizada. Além disso, também obtemos uma cota superior e inferior para a energia livre a volume infinito. Finalmente, utilizando argumentos de dualidade em grafos e expansão em alta temperatura estudamos o modelo de Potts acoplado as triangulações causais. Essa abordagem permite generalizar o modelo, melhorar os resultados obtidos para o modelo de Ising e obter novas cotas, superior e inferior, para a energia livre e para a curva crítica. Além disso, obtemos uma aproximação do autovalor maximal do operador de transferência a baixa temperatura.
Navarrete, Manuel Alejandro Gonzalez. "Modelo de Ising ferromagnético com campo externo periódico." Universidade de São Paulo, 2015. http://www.teses.usp.br/teses/disponiveis/45/45133/tde-28082015-000711/.
Full textWe study the low-temperature phase diagram for a ferromagnetic Ising model on $\\mathbb^2$, with a periodical external magnetic field. The external field takes two values: $h$ and $-h$, where $h>0$. The sites associated with positive and negative values of external field form a cell-board configuration with rectangular cells of sides $L_1\\times L_2$ sites, such that the total value of the external field is zero. As a main result, we show the presence of a first-order phase transition. The phase transition holds if $h<\\frac+ \\frac$, where $J$ is an interaction constant. We use the reflection positivity (RP) method. We apply a key inequality which is usually referred to as the chessboard estimate. Furthermore, we prove uniqueness for Gibbs measure in $h>4J$, using a uniqueness condition obtained in terms of disagreement percolation.
Santos, Ricardo Paupitz Barbosa dos. "Modelo de Ising diluído na rede de Bethe." Universidade de São Paulo, 2002. http://www.teses.usp.br/teses/disponiveis/43/43134/tde-09082017-155024/.
Full textThe site diluted Ising model is studied on a Beth lattice. The hierarchical structure of the Bethe lattice leads naturally to recursion relations obeyed by the probability distributions of the effective fields. The thermodynamic quantities on the Bethe lattice are then explicitly written in terms of the limiting distributions of the effective fields. Numerically exact results (i.e. if we neglect roundoff errors) for the distributions of the effective fields for T = 0 are presented, together with analytic results for select cases. It is found that the number of effective fields is always finite in the case of ferromagnetic interactions , but it might diverge for irrational values of the applied field in the case of antiferromagnetic interactions. These results yeld a numerically exact applied field versus concentration phase diagram for diluted antiferromagnet at T = 0. The distributions of the effective fields are computed aproximately for T > 0 and used to evaluete various thermodynamic quantities. Curves for the magnetization, free energy, internal energy and entropy are displayed. These calculations give an approximate three-dimensional phase diagram in the space of applied field, temperature and concentration.
Júnior, José Emílio de Lucena. "Modelo de Ising aplicado ao estudo da criminalidade." Universidade de São Paulo, 2014. http://www.teses.usp.br/teses/disponiveis/100/100132/tde-02042015-160340/.
Full textOur study was drawn from an analogy of the Ising model in two dimensions to analyze the influence that the network and the external forces can exert on the individual so that whether or not he intends to act lawfully. This study was inspired by that proposed in the article \"Analysing Tax Evasion Dynamics Via The Ising Model\" (ZAKLAN; WESTERHOFF; STAUFFER, 2009) model, but with emphasis on the intention of the agents, which precedes the criminal conduct, not to the commission of the crime itself, when the damage has already occurred to society. The analogy is the inclusion of some variables that model allowed us to study, according to each scenario, ways to maintain or reduce crime rates, predict possible situations hysteresis, their consequences and potential costs to society and the government.
Frazão, Camila Ribeiro. "Modelo de Ising em sistemas núcleo/casca nanomagnéticos." reponame:Repositório Institucional da UnB, 2014. http://repositorio.unb.br/handle/10482/17063.
Full textSubmitted by Ana Cristina Barbosa da Silva (annabds@hotmail.com) on 2014-11-25T15:19:10Z No. of bitstreams: 1 2014_CamilaRibeiroFrazao.pdf: 2148462 bytes, checksum: 736693a12406451fd34fa93a41a72f4e (MD5)
Approved for entry into archive by Patrícia Nunes da Silva(patricia@bce.unb.br) on 2014-11-26T11:42:46Z (GMT) No. of bitstreams: 1 2014_CamilaRibeiroFrazao.pdf: 2148462 bytes, checksum: 736693a12406451fd34fa93a41a72f4e (MD5)
Made available in DSpace on 2014-11-26T11:42:46Z (GMT). No. of bitstreams: 1 2014_CamilaRibeiroFrazao.pdf: 2148462 bytes, checksum: 736693a12406451fd34fa93a41a72f4e (MD5)
Neste trabalho foi realizada a investigação do diagrama de fase de partículas presentes em sistemas magnéticos nanoscópicos influenciados por capas que respondem à exposição de campos magnéticos. Foi utilizado o Modelo de Ising para representar o sistema magnético e o Método Monte Carlo com o Algoritmo de Metrópolis para obtenção das grandezas físicas mais relevantes. Levou-se em conta 4 diferentes estruturas, 3 bidimensionais: quadrada, triangular, tipo colmeia e 1 tridimensional: cúbica. Considerou-se apenas a influência dos primeiros vizinhos na rede e foi utilizado um modelo diferenciado de distribuição de intensidades dos momentos magnéticos ao longo da rede. A análise das curvas das propriedades magnéticas das estruturas, em particular das medidas da suscetibilidade magnética e do calor específico, permitiram identificar sucessivas transições de fase em baixas temperaturas. As transições de fase referentes às camadas da rede na simulação possibilitaram a elucidação do comportamento das curvas de propriedades magnéticas encontradas experimentalmente. _________________________________________________________________________________ ABSTRACT
In this work was made an investigation about the particle phase diagramresident in nanoscopic magnetic fields influenced by cases that respond toexposition of magnetic fields. The Ising model was used to represent the magneticsystem and the Monte Carlo method with the Metropolis algorithm to obtain themost relevant physical quantities. We took into account four different structures:square, triangular, honeycomb and cubic, taking into account just the influence ofthe first neighbors in the network and using a different model of intensitydistribution of the magnetic moments along the network. The analysis of thecurves of the magnetic properties of the structures, in particular of themeasurements of the magnetic susceptibility and of the specific heat, allowed usto identify successive phase transitions in low temperatures. The phase transitionsrelated to the network layers in the simulation allowed the elucidation about thebehavior of the curves of the magnetic properties founded throughexperimentation.
Ye, Feng. "Random-field ising ordering above magnetic vacancy percolation /." Diss., Digital Dissertations Database. Restricted to UC campuses, 2003. http://uclibs.org/PID/11984.
Full textMoreira, Antonio Flavio Barbosa. "Magnetismo de superficie em sistemas compressiveis de Ising." reponame:Repositório Institucional da UFSC, 1991. http://repositorio.ufsc.br/xmlui/handle/123456789/75718.
Full textMade available in DSpace on 2012-10-16T03:47:45Z (GMT). No. of bitstreams: 0Bitstream added on 2016-01-08T17:10:48Z : No. of bitstreams: 1 84767.pdf: 1765574 bytes, checksum: 20023fc08eb7998d91be1d5d091296e5 (MD5)
Neste trabaho estudamos o modelo de Ising em uma rede cúbica semi-infinita. Consideramos um modelo magneto-elástico com uma pressão uniaxial, onde os íons vibram somente em uma direção perpendicular aos planos cristalinos. Na aproximação de campo médio determinamos o diagrama de fases para os acoplamentos críticos de superfície em função da pressão, e o perfil da magnetização. Utilizando o grupo de renormalização de campo médio determinamos as superfícies críticas do modelo de Ising na rede cúbica semi-infinita considerando blocos de até 25 spins. O resultados que obtivemos para o acoplamento crítico de superfície é comparável àquele obtido através de simulação de Monte Carlo nesse mesmo modelo.
Santos, Marcio. "Transições de fase em modelos de ising cineticos." reponame:Repositório Institucional da UFSC, 1994. http://repositorio.ufsc.br/xmlui/handle/123456789/76022.
Full textMade available in DSpace on 2012-10-16T06:39:06Z (GMT). No. of bitstreams: 0Bitstream added on 2016-01-08T19:13:28Z : No. of bitstreams: 1 97845.pdf: 1679736 bytes, checksum: 7ce84e5cb3ceda57783814ee7b99fcc2 (MD5)
Neste trabalho estudamos dois problemas relativos à transição de fases em modelos magnéticos através da equação Mestra. No primeiro deles, consideramos a evolução, em direção ao estado estacionário, de uma cadeia dupla de spins, através da relaxação inicial do parâmetro de ordem. Mostramos que o expoente crítico dinâmico pode depender dos aspectos microscópicos da Hamiltoniana, não exibindo um caráter universal, para as taxas de transição de Glauber e Kawasaki. No segundo problema determinamos os estados estacionários para o modelo de Ising anisotrópico em duas dimensões, levando-se em conta a correlação entre primeiros vizinhos. Determinamos o diagrama de fases desse modelo, que apresenta as fases antiferro, ferro e paramagnética.
Campos, Paulo Roberto de Araujo. "Comportamento crítico dinâmico de algoritmo de Wolff no Modelo de Ising com correlação de sítios e ligações." Universidade de São Paulo, 1998. http://www.teses.usp.br/teses/disponiveis/76/76131/tde-10092008-092104/.
Full textWe extend the Wolff Algorithm to include correlated spin interactions in diluted magnetic systems. This algorithm is applied to study the site-bond-correlated Ising model on a two-dimensional square lattice. We use a finite-size scaling procedure to obtain the phase diagram in the temperature-concentration space. Our results are in excellent agreement with the experimental data for the Knip Mg1-pF3, compound. We also present the critical dynamical behavior of the Wolff algorithm for this system. We have verified that the autocorrelation time diminishes in the presence of dilution and correlation, showing that the Wolff algorithm performs even better in such situations. This behavior is completely different from those exhibited by the single spin-flips algorithms.
Dillmann, Oliver. "Monte-Carlo-Simulationen zum kritischen Verhalten dünner Ising-Filme." [S.l.] : [s.n.], 2000. http://ArchiMeD.uni-mainz.de/pub/2000/0071/diss.pdf.
Full textGibson, Sarah. "Merchant-ising England : the cultural consumption of the Englishness." Thesis, Lancaster University, 2003. http://ethos.bl.uk/OrderDetails.do?uin=uk.bl.ethos.423929.
Full textEckner, Sinziana Maria. "Stochastic Ising Models at Zero Temperature on Various Graphs." Thesis, New York University, 2014. http://pqdtopen.proquest.com/#viewpdf?dispub=3665138.
Full textIn this thesis we study continuous time Markov processes whose state space consists of an assignment of +1 or -1 to each vertex x of a graph G. We will consider two processes, σ( t) and σ'(t), having similar update rules. The process σ(t) starts from an initial spin configuration chosen from a Bernoulli product measure with density θ of +1 spins, and updates the spin at each vertex, σx(t), by taking the value of a majority of x's nearest neighbors or else tossing a fair coin in case of a tie. The process σ'( t) starts from an arbitrary initial configuration and evolves according to the same rules as σ(t), except for some vertices which are frozen plus (resp., minus) with density ρ+ (resp., & ρ–) and whose value is not allowed to change. Our results are for when σ(t) evolves on graphs related to homogeneous trees of degree K ≥ 3, such as finite or infinite stacks of such trees, while the process σ'(t) evolves on Zd, d ≥ 2. We study the long time behavior of these processes and, in the case of σ'(t), the prevalence of vertices that are (eventually) fixed plus or fixed minus or flippers (changing forever). We prove that, if θ is close enough to 1, σ(t) reaches fixation to +1 consensus. For σ'( t) we prove that, if ρ+>0 and ρ– = 0, all vertices end up as fixed plus, while for ρ+ >0 and ρ– very small (compared to ρ +), the fixed minus and flippers together do not percolate.
Jiménez, Ramírez Andrea Patricia. "Estados Satisfactorios del Modelo de Ising Antiferromagnético en Triangulaciones." Tesis, Universidad de Chile, 2012. http://www.repositorio.uchile.cl/handle/2250/102786.
Full textFilho, Raimundo Valmir Leite. "Impurezas MagnÃticas em Ferromagnetos de Ising com Campo Transverso." Universidade Federal do CearÃ, 2005. http://www.teses.ufc.br/tde_busca/arquivo.php?codArquivo=2917.
Full textFundaÃÃo de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do CearÃ
O formalismo de funÃÃes de Green à usado para calcular o espectro de excitaÃÃes associados a impurezas magnÃticas implantadas em um filme ferromagnÃtico descrito pelo modelo de Ising com campo transverso. AtravÃs do mÃtodo da equaÃÃo de movimento expressÃes explÃcitas para as funÃÃes de Green sÃo determinadas para um ferromagneto sem impurezas. A funÃÃo de Green para um filme ferromagnÃtico contendo impurezas à obtida atravÃs da equaÃÃo de Dyson. O espectro de ondas de spin relativo Ãs impurezas à obtido para freqÃÃncias abaixo do limite inferior da banda de volume para um material puro. Com o objetivo de avaliar a influÃncia da posiÃÃo das impurezas no filme no espectro de excitaÃÃes, consideramos trÃs diferentes disposiÃÃes geomÃtricas para as impurezas: linha de impurezas perpendicular à superfÃcie do filme, quatro impurezas em um plano paralelo `as superfÃcies e quatro impurezas em um plano perpendicular `as superfÃcies do filme. Obtemos resultados para a freqÃÃncia dos modos localizados como funÃÃo do parÃmetro de troca entre duas impurezas vizinhas, do parÃmetro de troca entre as impurezas e seus vizinhos e do parÃmetro de campo efetivo nas impurezas.
A Green function formalism is used to calculate the spectrum of excitations associated with magnetic impurities implanted in a ferromagnetic thin film described by the transverse Ising model. Using the equations of motion method, explicit expressions for the Green function are determined for a ferromagnetic without impurities. The Greenâs functions for a ferromagnetic film containing impurities are obtained through Dyson equation. We consider only the âdefectâ modes that appear below the bulk band of the pure material. In order to assess the influence of the position of the impurities in the film on the excitations spectra, we consider three different geometrical arrangement for the impurities: impurities line perpendicular to the surface film, four impurities in a plane paralel to the surface, and four impurities in a plane perpendicular to the surfaces of the film. We obtain results for the frequencies localized modes as a function of the exchange parameter between two impurities neighborings, of the exchange parameter between the impurities and their neighborings, and the effective field parameter at the impurities.







